The Key Factors that Influence Solar Panel Cost and Efficiency As the demand for renewable energy grows, solar panels are becoming one of the most reliable and widely adopted solutions. With improvements in technology, the cost of solar panels has dropped significantly over the past decade while their efficiency has improved. This makes them a strong investment for both households and businesses.
In this guide, we’ll break down the main factors that affect the cost and efficiency of solar panels, so you can better evaluate whether installing a solar system is the right choice for you.
What Determines Solar Panel Cost and Efficiency?
1. Type of Solar Panels
Different Types of Solar Panels are available, each with its own cost, pros and cons:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: These are made from a single continuous crystal structure and are known for their high efficiency and sleek appearance. They tend to be more expensive but offer the best efficiency.

- Polycrystalline Solar Panels: These panels are made from multiple silicon crystals and are generally less efficient than monocrystalline panels. However, they are more affordable, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers.

- Thin-Film Solar Panels: These panels are made from a variety of materials and are the least expensive. They are flexible and lightweight but offer lower efficiency compared to crystalline panels.

2. Installation Cost
The cost of installing solar panels includes several components:
- Labor Cost: Skilled labor or solar energy technician are required to install solar panels correctly. Labor costs can vary based on location and the complexity of the installation.
- Mounting Systems: The type of roof and the mounting system needed can affect costs. For example, installing panels on a flat roof may require a different setup than a sloped roof.
- Permitting and Inspection: Obtaining necessary permits and passing inspections can add to the overall cost.
3. Inverter Cost
Solar Inverters are essential components that convert the Direct Current (DC) produced by solar panels into Alternating Current (AC) used in homes. There are different types of inverters, such as string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers, each with varying costs.
4. Battery Cost
2 types of Solar Batteries are available:
- Flat Plate Battery; and
- Tubular Battery
Tubular batteries are taller than flat plate batteries. They are manufactured by using three main chemical compositions: lead acid, lithium ion, and saltwater. Lithium ion batteries are very successful and best option for a home solar panel system.
Following are the 4 major types of solar batteries available:
| # | Battery Type | Pros and Cons |
| 1. | Lithium ion battery | Higher battery energy density but expensive |
| 2. | Lead acid battery | Cheapest energy storage option but require regular maintenance. |
| 3. | Flow battery | 100% depth of discharge but low storage capacity and expensive. |
| 4. | Nickel cadmium battery | Durable and perform well in extreme temperatures but extremely toxic. |
5. Cost of Additional Equipment
Other necessary equipment like mounts, monitoring systems, and wiring can also impact the total cost of a solar panel system.
6. Government Incentives and Subsidy
Government incentives, tax credits, and rebates can significantly reduce the cost of installing solar panels. PM Solar Rooftop Muft Bijli Yojana one such scheme in India that aims to encourage installation of solar panels on rooftops and adoption of solar energy by providing various benefits, including subsidies and financial incentives. Check your local, state, and federal programs to maximize your savings.
Cost Range of Different Types of Solar Panels
| # | Type of Solar Panel | Cost Range (per watt) |
| 1. | Monocrystalline Solar Panels | $0.35 to $0.90 |
| 2. | Polycrystalline Solar Panels | $0.30 to $0.75 |
| 3. | Thin-Film Solar Panels | $0.25 to $0.70 |
| 4. | Bifacial Solar Panels | $0.40 to $1.00 |
Cost of Solar Panels for 1,2,3,4,5 Bedroom House
| # | House Size | Average Solar Panel System Size (kW) | Average Cost (USD) |
| 1. | 1 Bedroom | 3 – 4 kW | $9000 – $12,000 |
| 2. | 2 Bedroom | 4 – 5 kW | $12,000 – $15,000 |
| 3. | 3 Bedroom | 5 – 6 kW | $15,000 – $18,000 |
| 4. | 4 Bedroom | 6 – 7 kW | $18,000 – $21,000 |
| 5. | 5 Bedroom | 7 – 8 kW | $21,000 – $24,000 |
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
1. Panel Material and Design
- Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline: As mentioned earlier, monocrystalline panels are generally more efficient than polycrystalline panels due to their pure silicon composition.
- Cell Technology: Innovations in cell technology, such as PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) and bifacial panels, can enhance efficiency.
2. Temperature Coefficient
Solar panels operate more efficiently at lower temperatures. The temperature coefficient indicates how much a panel’s efficiency decreases with rising temperatures. Panels with a lower temperature coefficient perform better in hot climates.
3. Shade Tolerance
Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce a solar panel’s efficiency. Panels equipped with microinverters or power optimizers can minimize the impact of shading.
4. Orientation and Tilt
The direction and angle at which panels are installed affect their exposure to sunlight. South-facing panels with an optimal tilt angle generally receive the most sunlight and, therefore, perform better.
5. Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial for maintaining solar panel efficiency. Dust, dirt, and debris can obstruct sunlight and reduce a panel’s performance.
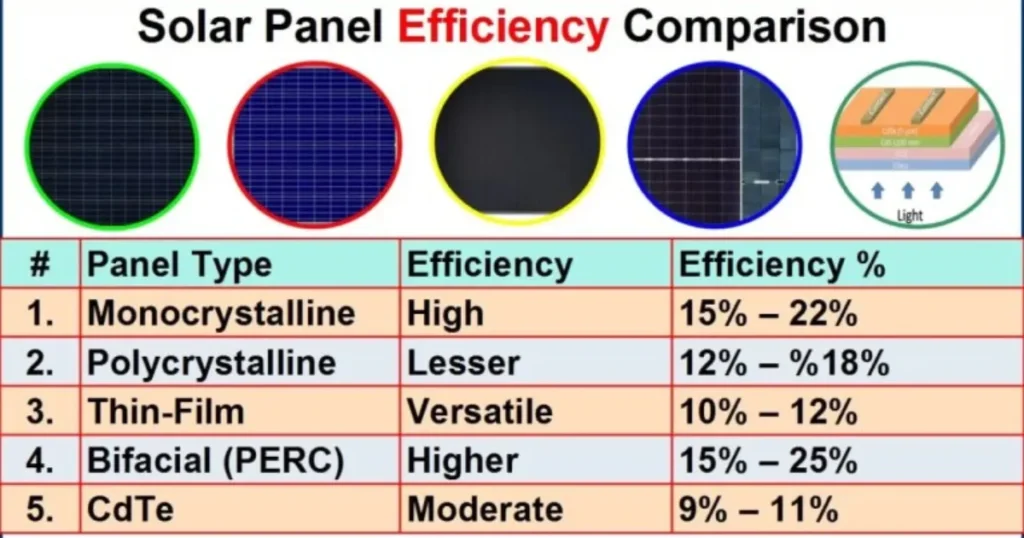
Types of Solar Panels, Cost, Efficiency, Lifespan
Here is a table showing different types of solar panels available in the market, their cost, efficiency and lifespan.
| # | Panel Type | Cost | Efficiency | Lifespan |
| 1. | Monocrystalline | High | 15-22% | Upto 25 Years |
| 2. | Polycrystalline | Moderate | 12-18% | Upto 25 Years |
| 3. | Thin-Film | Low | 10-12% | 10-20 Years |
Solar Panel Efficiency Chart
Solar Panel Efficiency Over Time Graph (1990-2023)
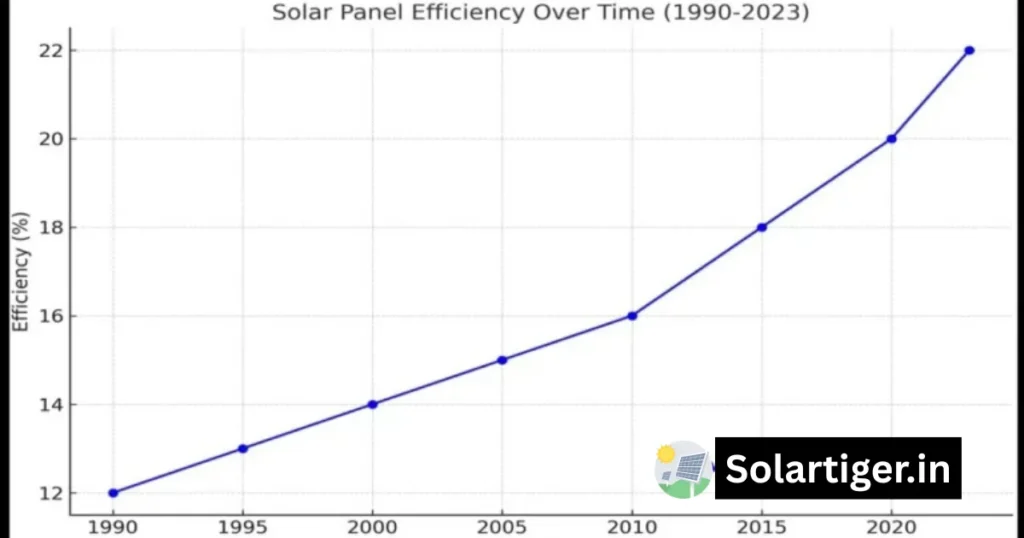
Here is graph showing solar panel efficiency over time from 1990 to 2023.
Solar Panel Efficiency Formula
The efficiency of a solar panel can be calculated using the following formula:
η = Pout / Pin × 100%
Where:
- η is the efficiency of the solar panel,
- Pout is the electrical power output of the solar panel (in watts),
- Pin is the power of the incident sunlight on the panel (in watts).
The power of the incident sunlight Pin can be calculated using the formula:
Pin = A × G
Where:
- A is the area of the solar panel (in square meters),
- G is the solar irradiance (the power per unit area received from the Sun, typically measured in watts per square meter).
Combining these, the efficiency formula of solar panel can be expressed as:
η = (Pout / A × G) × 100%
So we can say that, the efficiency of a solar panel is the ratio of the electrical power it produces to the power of the sunlight it receives, adjusted for the area of the panel and expressed as a percentage.
Solar Panel Efficiency Improvements Over Time
Over the years, solar panel efficiency has seen remarkable improvements, revolutionizing the renewable energy sector. Advances in photovoltaic technology, such as the development of monocrystalline and bifacial solar cells, have significantly boosted energy conversion rates. Innovations like passivated emitter and rear cell (PERC) technology have further enhanced performance, pushing efficiencies above 22%.
Continuous research and development aim to reduce costs while increasing the lifespan and efficiency of solar panels, making solar energy a more viable and sustainable solution for global energy needs. These technological advancements promise a brighter, greener future powered by solar energy.
Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI)
When considering solar panels, it is important to calculate the ROI to understand the financial benefits over time. Here is a simplified formula to estimate ROI:
ROI = (Total Savings from Solar Energy / Total Cost of Solar System) × 100
* Total savings include reduced electricity bills and any available incentives or rebates.
Conclusion
Investing in solar panels involves considering various factors that affect costs and efficiency. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions that maximize your solar investment benefits. As technology continues to advance, the future of solar energy looks promising, offering a cleaner, more sustainable energy solution for all.